Although organizational innovation is neglected in scientific studies, companies are taking more and more notice of the importance of organizational innovations such as the adoption of artificial intelligence, open office workplace, automated processes, cloud solutions, etc. MIT’s study of the automobile industry in Japan, the USA and Germany, published in the late 1980s, was first to attract scientist’s and manager’s attention towards organizational innovation as the driving factor to achieve better performance and competitiveness.
When it comes to organizational innovation, we tend to see it and understand it as an organizational change within the company/organization. The literature is full of attempts to categorize different types of innovation, so let’s take a look at the organizational innovation as defined by Oslo Manual which categorizes innovation types as an object of the innovation.
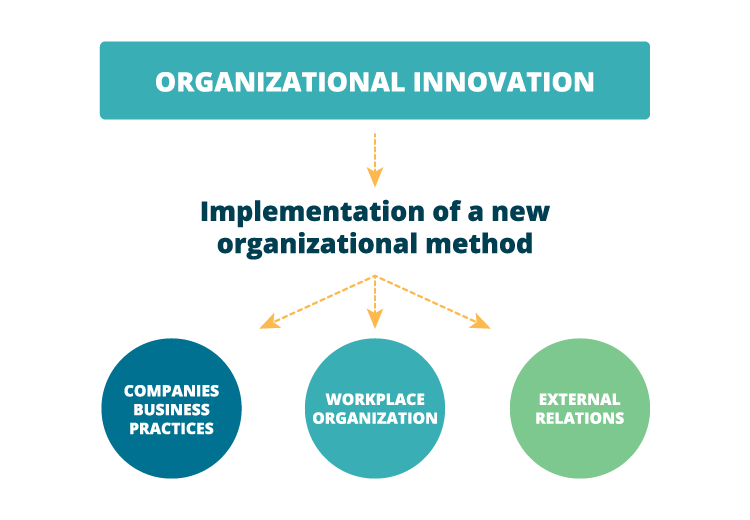
Oslo Manual defines organizational innovation as the implementation of a new organizational method in:
- company’s business practices,
- workplace organization or
- external relations.
Organizational innovation is aimed at increasing the company’s performance by reducing administrative or transaction costs, improving the workplace satisfaction and therefore employee’s productivity, or even reducing the supply costs. The main difference between organizational innovation and organizational change is in the implementation of an organizational method that was not previously used within the company. Organizational change may not necessarily involve innovations as many companies change their structure or strategy without actually being innovative in the execution of the said change. Organizational innovation is always the result of strategic decisions made by the senior management.
When a company implements new methods for organizing the work routines and procedures, then we are speaking about organizational innovations in business practices. The most known example is the introduction of lean manufacturing production (lean), with the main characteristics being simultaneous engineering and just-in-time delivery, which have been discovered to be the number one reason for the Japanese car industry excellence. The lean approach can systematically identify and eliminate segments in the production activities that do not add value. Since its invention, lean has been successfully applied in the manufacturing and non-manufacturing sectors, such as banking, hospitals, education, government, administration, insurance and health.
Today, companies worldwide adopt business solutions powered by AI with the aim to reduce costs and improve productivity. The workforce is deeply affected by all this change, and smart organizations are taking steps not just to implement intelligent technologies but also to recruit and retrain people for skilled roles, redesign tasks and jobs, and use AI as an enabler of innovation in products, processes, and business models.
The implementation of new methods for distributing responsibilities and decision making among employees, as well as new concepts for structuring activities such as integration of different business activities represent organizational innovations in workplace organization.The cloud-based innovation management solution is a great example of an organizational model that introduces structure to your innovation processes, while giving employees greater autonomy in decision making and encourages them to contribute with their ideas. Increased collaboration and engagement of the employees have a beneficial impact because participation in decision-making is more likely to lead to a better judgment, and, potentially, more productive outcomes. Also, an example of organizational innovation in structuring business activities would be the implementation of a built-to-order productions systems, with the end goal of integrating sales and production processes.
As the company’s external relations are very important part of every business strategy, the implementation of new ways of organizing those relations represents organizational innovation as well. These include, for example, the establishment of new types of cooperation with universities, research organizations and government institutions. Other examples would be implementation of new methods for collaboration with customers, new methods of integration with suppliers, or outsourcing business activities in production, distribution, procuring and recruiting.
The implementation of organizational innovation in a company is a challenging task that depends on many factors, such as the company strategy and culture, the context the company is embedded in, and market where the company operates. Important characteristic of organizational innovation is close relationship to product or process innovations. New products often need some new production processes, which require new organizational structures. Organizational innovation also supports technological innovation, as it tends to trigger the adoption of technological innovation. Another important characteristic is their social dimension, since they affect the company culture and involve employees in the process.
Organizational innovation in Samsung was introduced by long-time CEO Jong-Yong Yun, that opened design centers around the world with the aim to give his creative employees direct access to top management and space to develop new products. Compared to traditional South Korean culture that does not allow employees to freely express their ideas, this was the first time for employees to have their ideas be heard by the Executive Board. This way Samsung developed a New Concept Development process that all business units can implement, and develop solution concepts based on employees’ ideas, consumers opinion, and market-driven technologies.
According to 2016 Gartner Financial Services Innovation Survey, "the biggest threat to innovation is internal politics and an organizational culture which doesn’t accept failure, doesn’t accept ideas from outside, and/or cannot change."
So, how do you handle the complex process of organizational innovations?